Recently, the 37th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs (ISPSD) was held in Kumamoto, Japan. The research paper titled "The Latest Fabrication and Experimental Results of 1.2 kV Split-Gate 4H-SiC MOSFET with P+ Buffer", presented by the Team of Advanced Power Conversion and Electrified Transportation Systems from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Applied Electronics, showcased Tsinghua University’s latest research achievements in the field of power semiconductors. The paper received widespread recognition from both industry and academic experts. The first author of the paper is Chen Yuzhi, a Ph.D. student from the 2023 class at EEA, and the corresponding author is Associate Professor Zheng Zedong. This marks the first time Tsinghua University has published a paper as the first completion unit at the ISPSD conference.
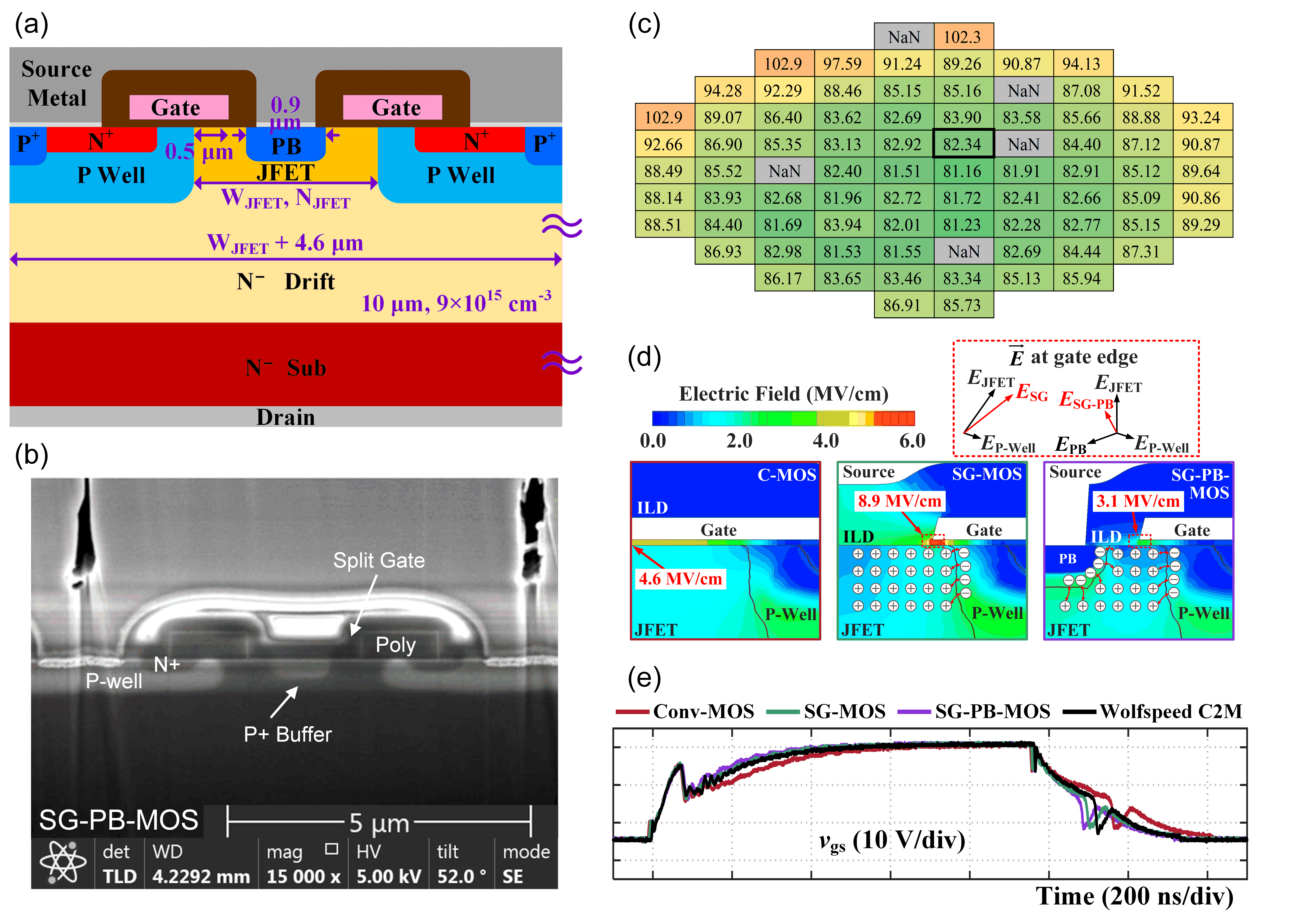
The paper details the Split-Gate SiC MOSFET with an integrated P+ buffer layer. The structure includes (a)-(b) device structure diagrams, (c) wafer resistance distribution, (d) charge coupling effect schematic, and (e) measured switching waveform.
Silicon carbide metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (SiC MOSFETs) have brought revolutionary changes to fields such as new energy vehicles, renewable energy generation, and smart grids, due to their excellent properties like high voltage, high frequency, and low conduction loss. To further improve the switching speed and reliability of SiC MOSFETs, Zheng Zedong’s research team proposed a new structure, the Split-Gate SiC MOSFET with an integrated P+ buffer layer (SG-PB-MOS), and successfully completed the wafer fabrication and experimental validation for a 1200V/80mΩ grade device. By integrating a P+ buffer injection layer in the cell JFET region and utilizing charge coupling effects, the device’s performance was significantly optimized: the peak gate oxide electric field intensity decreased by 32.6%, short-circuit tolerance time increased by 26.8%, gate-drain capacitance reduced by 64.3%, and the high-frequency figure of merit (HF-FOM) improved by 3.01 times. In comparison with Wolfspeed’s C2M 1200V/80mΩ series product, which uses the same layout, the device developed by EEA’s team showed superior dynamic performance with a significantly improved gate switching speed. Moreover, the device structure is compatible with existing process platforms, with a high wafer yield rate of 94%, demonstrating excellent potential for engineering applications and providing innovative solutions for high-efficiency, high-reliability, and high-power-density SiC-based converters. The core technologies related to this device have been patented in China.
Ph.D. student Chen Yuzhi took a photo with the poster at the conference.
About IEEE ISPSD
IEEE ISPSD is the most influential and largest international academic conference in the field of power devices. It is often referred to as the "Olympic Conference" in this field due to its strict paper selection process and focus on both innovation and practical applicability. Many milestone technological breakthroughs in power devices have been first presented at ISPSD. This year’s conference (ISPSD 2025) covered high-voltage/low-voltage power devices, power ICs, packaging, wide-bandgap semiconductors (SiC/GaN), and other fields, showcasing the latest excellent research achievements and progress in global power semiconductor technology. A total of 176 high-quality papers were accepted, attracting over 600 scholars and engineers. ISPSD is held annually in Europe, Japan, North America, and other regions, with Kumamoto, Japan as the venue for 2025, and Las Vegas, USA, as the venue for 2026.












 News & Events
News & Events