Recently, the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IEEE IES) Annual Conference was held in Madrid, Spain. Doctoral student An Feng from Tsinghua University’s Department of Electrical Engineering and Applied Electronics (EEA), currently a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Queensland, Australia, was the first author, and Associate Professor Zhao Biao of the EEA served as the corresponding author. Their paper, “DC Cascaded Energy Storage System Based on DC Collector With Gradient Descent Method,” published in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (IEEE TIE), won the 2025 IEEE Student Best Paper Award.

IEEE TIE was founded in 1953 and is sponsored by the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IES). It is a top international journal in engineering, automation systems, and electronics/electrical fields, with a latest impact factor of 7.2 and classified as a top-tier journal (Category I) by the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The Student Best Paper Award was established in 2005 to recognize outstanding student papers published in IES journals or major conferences, encouraging students and graduate authors to continue research in industrial electronics. In 2024, IEEE TIE published 1,608 papers. After nomination by the editorial board, recommendation by the Editor-in-Chief, evaluation by the award committee, and discussion by the IEEE IES AdCom, only this paper received the Student Best Paper Award for the year.

Facing challenges to grid stability posed by renewable energy integration and the need for large-capacity battery storage connection to the grid, the research team focused on DC energy storage system topology and control technologies, aiming to overcome bottlenecks of traditional solutions such as high cost, voltage imbalance, and harmonic interference. Traditional modular DC transformer (DCT)-based solutions require two-stage power conversion for storage access, leading to low efficiency and poor economics, as well as series voltage imbalance issues. Improved cascaded DCT solutions or those including Power Balancing Units (PBU) still face challenges of high voltage stress, uncontrollable fault currents, or excessive PBU capacity.
The paper innovatively proposes a “DC Cascaded Energy Storage System Based on DC Collector”. By using the DC collector’s multiple dispersed low-voltage ports and centralized medium-voltage ports, low-voltage storage batteries are directly connected to the medium-voltage DC bus. Combined with variable-carrier phase-shift modulation based on gradient descent, dominant current harmonics are suppressed. This design eliminates the need for additional power balancing units and large LC filters, reducing cost while improving power density, providing a new pathway for large-scale energy storage deployment.
The work focuses on DC collector topology design, submodule selection optimization, and harmonic control methods, enabling efficient large-scale battery integration into DC grids. It meets the demands of renewable energy absorption and enhances the techno-economic performance, power density, and operational efficiency of energy storage systems.
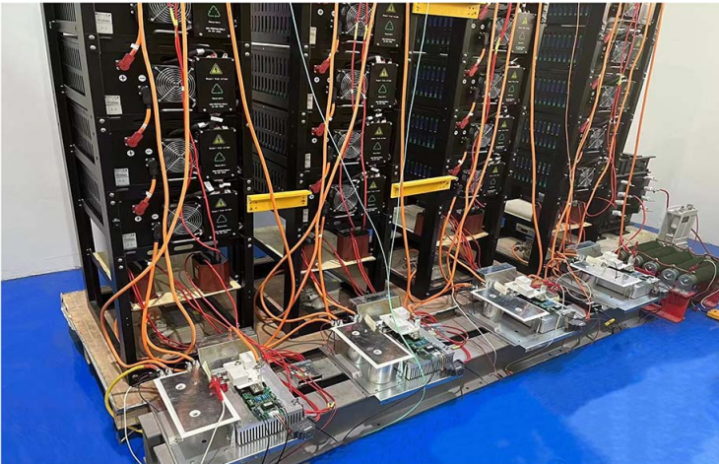
Awarded Paper Link:
https://iten.ieee-ies.org/announcement/2025/2025-ieee-industrial-electronics-society-paper-awards-announced/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=2025-ieee-industrial-electronics-society-paper-awards-announced
An Feng, PhD, Tsinghua University; Postdoctoral Researcher, University of Queensland, Australia; recognized as a top 2% scientist globally by Stanford/Elsevier in 2024; recipient of the Geneva Invention Exhibition Gold Award. His research focuses on renewable energy power conversion, power electronic converter topology and control, and optimal operation and modeling of power systems with power electronic equipment. He has published more than 20 papers in top journals including IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics and IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, and holds over 10 granted invention patents.












 News & Events
News & Events